What is NgRx?
NgRx is a framework wrote with TypeScript, to help building "Reactive Angular Applications".NgRx main features: State management, Isolation of side effects, Entity collection management
When to choose NgRx?
| Pros | Description |
|---|---|
| Single source of truth | Because all state is stored in a single object tree |
| Testability | All function is Pure, help a lot when testing |
| Scaleable | A lot better than vanila Angular |
| Cons | Description |
|---|---|
| Write extra code when start project | Have to write all code as NgRx structure and syntax |
| Extra knowledge for developer | Developer need to learn NgRx before join project |
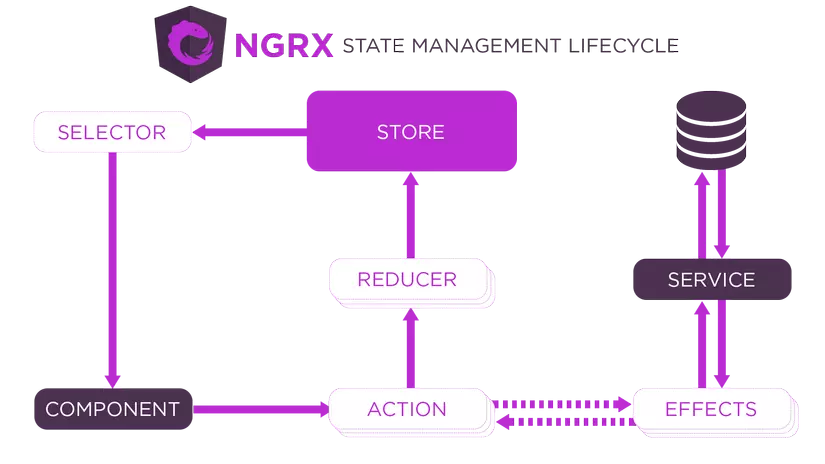
Main concept
Store: as it name, Store is the place to store all state. (It's a tree object)
Action: Define an action (a string and optional data related), for changing some state
Reducer: Take current state and action, then Execute the state changing.
Selectors: Pure Functions that retrieve specific pieces of state from the store.
Effects: Handle side effects, such as API calls.
Setting Up NgRx
To get started with NgRx, you need to install it in your Angular project. Use the Angular CLI to add NgRx:
ng add @ngrx/store
ng add @ngrx/effects
This command sets up the necessary files and configurations for NgRx in your project. After installation, you can configure the store in your app.module.ts:
import { StoreModule } from '@ngrx/store';
import { itemReducer } from './store/item.reducer';
@NgModule({
imports: [
StoreModule.forRoot({ items: itemReducer }),
// other imports
],
})
export class AppModule {}
Creating Actions and Reducers
Actions are the primary means of communicating with the store. You can define actions using the createAction function:
import { createAction, props } from '@ngrx/store';
export const loadItems = createAction('[Item List] Load Items');
export const loadItemsSuccess = createAction(
'[Item List] Load Items Success',
props<{ items: Item[] }>()
);
Reducers handle state changes based on actions. Here’s an example of a simple reducer:
import { createReducer, on } from '@ngrx/store';
import { loadItems, loadItemsSuccess } from './item.actions';
export interface ItemState {
items: Item[];
loading: boolean;
}
export const initialState: ItemState = {
items: [],
loading: false,
};
const itemReducer = createReducer(
initialState,
on(loadItems, (state) => ({ ...state, loading: true })),
on(loadItemsSuccess, (state, { items }) => ({ ...state, items, loading: false }))
);
Conclusion
In this post, we introduced the basics of NgRx, including its core concepts and how to set it up in an Angular application. Understanding these fundamentals will help you manage state effectively as your application grows. In the next post, we will dive deeper into intermediate concepts, including selectors and effects.